An asteroid larger than the Statue of Liberty will fly close to Earth at 8:20 PM GMT on Christmas Day, according to data from NASA. Near Earth Studies Center.
The asteroid, named 2014 SD224, will come within 0.02019 astronomical units, or approximately 1.9 million miles, from Earth’s surface.
The 2014 SD224 is between 302 and 690 feet (92 to 210 meters) in diameter – meaning it could be more than twice the size of the Statue of Liberty (305 feet) or larger than Salisbury Cathedral (404 feet).
Since the 2014 SD224 flies over Earth, it will travel at 10 kilometers per second or more than 22,000 miles per hour – nearly 30 times the speed of sound.
Despite being about eight times farther from the moon, the asteroid has been classified as a Near-Earth Object (NEO) and is being tracked by the space agency.
The asteroid could be more than twice the size of the Statue of Liberty (305 feet) or Elizabeth Tower (known as Big Ben) and larger than Salisbury Cathedral (404 feet)
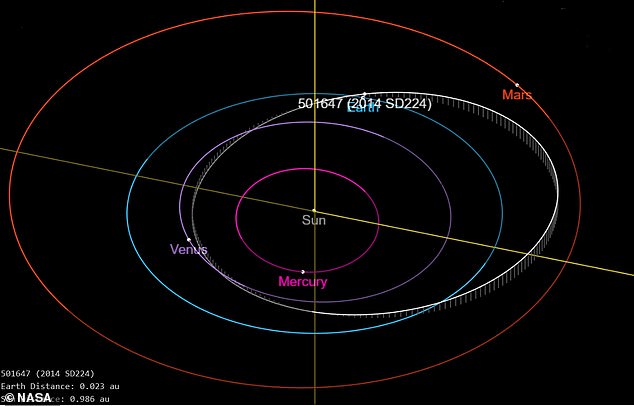
Asteroid 2014 SD224 (also known as 501647) and its trajectory relative to the orbits of the planets in our solar system. Earth’s orbit is light blue
Although 2014 SD224 – which can be Track it down on the NASA website At a distance of 1.9 million miles, this is relatively close astronomically.
For this reason, 2014 SD224 is identified by NEO, although no harm is expected.
A NEO is an asteroid or comet that its orbit brings to or through an area located between about 91 million and 121 million miles (195 million km) from the sun, which means that it can pass within 30 million miles (50 million km) of Earth’s orbit. .
If the object is larger than 460 feet (140 meters), it is considered a Potentially Dangerous Object (PHO).
NASA said: “Near-Earth objects are comets and asteroids that were pushed by the gravity of nearby planets into orbits that allow them to enter the neighborhood of Earth.”
Comets mostly consist of water ice with compact dust particles, and were originally formed in the cold outer planetary system while most of the rocky asteroids formed in the warmer inner solar system between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
Scientific interest in comets and asteroids is largely attributed to their status as the relatively unchanged remnant of the Solar System formation around 4.6 billion years ago.
to me Publicly available NASA data, 24,629 NEOs have been detected as of Tuesday.
It is estimated that there are about 25,000 NEOs larger than 460 feet (140 meters).
There are also an estimated 1,000 NEOs larger than 3,280 feet (one kilometer), highlighting the need to track these space rocks.
On average, Earth collides with a rock the size of a soccer field every 5,000 years, and an asteroid ends up with civilization every million years, according to NASA’s Near Earth Objects Program.

A NEO is an asteroid or comet that its orbit brings to or through an area located between about 91 million and 121 million miles (195 million km) from the sun, which means that it can pass within 30 million miles (50 million km) of Earth’s orbit. (Stock image)
“Through our constant search for asteroids, we would eventually expect to find the majority of asteroids 100 meters in diameter over time, with each occurring on our planet many years or decades before a potential impact,” says Paul Chodas, NASA Administrator. Near Earth Studies Center said Newsweek.
We’ve already stripped over 95 percent of really large asteroids (1 kilometer or 0.62 miles in size and larger) and know that none of them have any chance of impact over the next century.
Last month, an asteroid the size of a London bus was detected that missed Earth by 240 miles (386 km) – Friday the 13th.
The space rock, dubbed “ 2020 VT4, ” was spotted just 15 hours after its closest approach by the recent asteroid impact alert system on Mauna Loa, Hawaii.
Had it been so close, the object 16 to 33 feet (5 to 10 meters) wide would have burned in the atmosphere over the South Pacific Ocean.
Its orbit brought it as close to Earth as the International Space Station, making it the closest asteroid to pass Earth on record so far.

“Music specialist. Pop culture trailblazer. Problem solver. Internet advocate.”








