The new color images sent back by the James Webb Space Telescope have seen the light of day. Ten or so hours ago, the first image was presented, which shows the deepest and most detailed picture of the universe to date.
NASA displayed the first color image from the James Webb Telescope at night from Monday to Tuesday, Poland time. This was a snapshot of the galaxy cluster SMACS 0723. On Tuesday afternoon, a batch of back-to-back images of the universe were revealed.
First, the spectrum of the atmosphere of exoplanet WASP-96 b is shown. An extrasolar planet is a planet orbiting a star other than the Sun. Scientists have watched an exoplanet transit in front of their star and took this opportunity to pick out the spectrum of the planet’s atmosphere. The spectrum shows, among other things, signs of the presence of water vapor in the atmosphere of WASP-96 b, thanks to which it will be possible to determine how much is present.
We are 1,150 light-years away from this exoplanet. Its mass is about half that of Jupiter. It was discovered in 2014.
Atmospheric spectrum of egozplanet WASP-96 b orbiting a star 1,150 light-years away.NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI
Tuesday’s event included an image showing the Southern Ring Nebula (NGC 3132). This is a planetary nebula also known as the Shattered Eight Nebula. It’s a gas cloud around a dying star. According to NASA, the James Webb Telescope was the first to reveal that the star is covered in dust. Thanks to him, scientists will be able to closely study planetary nebulae.
The Southern Ring Nebula is about half a light-year in diameter and about 2,000 light-years away.
The Southern Ring Nebula (NGC 3132, also known as the Shattered Eight), or gas cloud around a dying starNASA, ESA, CSA, STScI
The image below shows the Stefan Quintet Cluster, a group of five galaxies. However, in reality, only four galaxies are close to each other (290 million light years from us), and the fifth is only optically close (40 million light years from us).
NASA reports that the image is made up of more than 150 million pixels and nearly 1,000 separate graphic files. This allows you to see unprecedented detail in this group of galaxies. The new image details how the interaction between galaxies spurs star formation to each other and how galaxies are disrupted.
Stefan Quintet, a group of galaxies 290 million light-years awayNASA, ESA, CSA, STScI
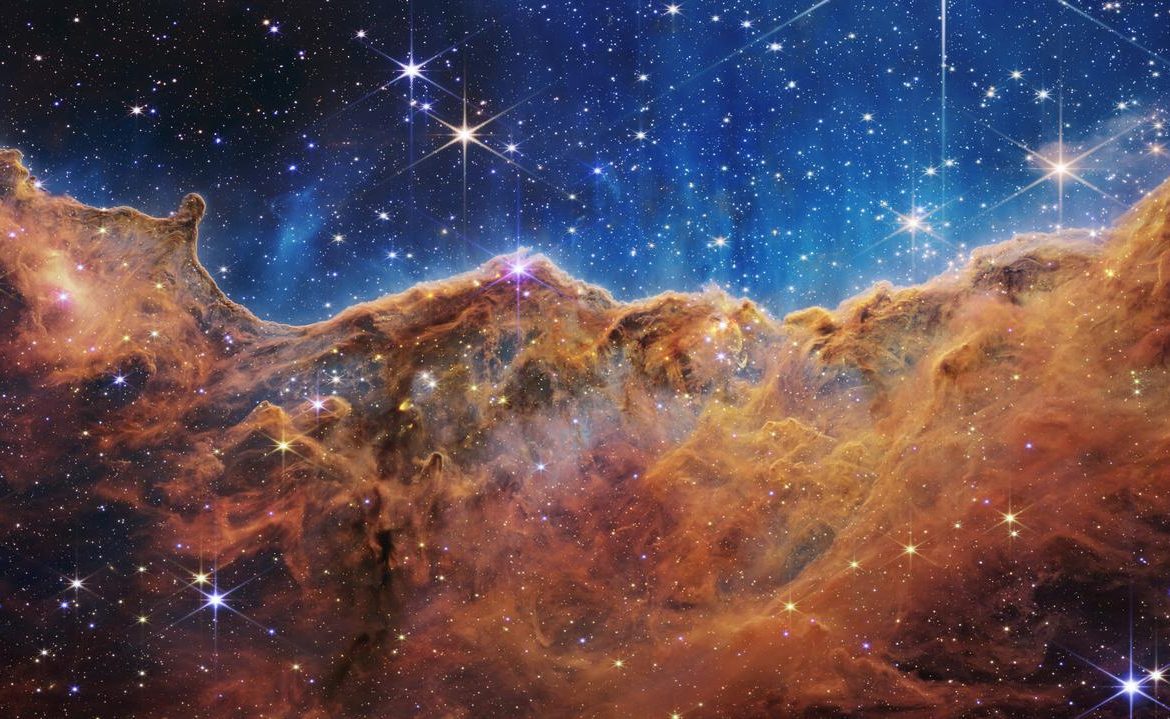
The last image, from the first color images taken by the James Webb Space Telescope, rendered shows the star-forming region of NGC 3324 in the Carina Nebula, specifically its edge. The image shows previously unseen stellar birth regions.
As noted by NASA, this shot resembles a landscape of mountains and valleys under a starry evening sky. This nebula is one of the largest and brightest. It is located about 7,600 light-years away in the constellation Kela.
The Carina Nebula, one of the largest and brightest nebulae in the skyNASA, ESA, CSA, STScI
The images and spectra shown were selected by an international panel composed of representatives from NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI).
The first image from the Webb Telescope
The first photo is on display at the White House. The event was attended by US President Joe Biden and Vice President Kamala Harris with NASA. As confirmed by the US space agency, “This is the deepest and most detailed image of the universe captured so far (…) showing the light of galaxies that took billions of years to reach us.”
The photo was called Webb’s First Deep Field. It is represented by the galaxy cluster SMACS 0723, which is 4.5 billion light-years away from us. The cluster acts as a gravitational lens, distorting and amplifying images of distant galaxies behind it.
At least one beam of ancient faint light rays appearing on the image’s “background” – made up of images of different wavelengths – dates back more than 13 billion years, NASA chief Bill Nelson said. “It’s a small part of the universe,” Nelson added.
The displayed image was created from observations with a total exposure time of 12.5 hours. In terms of infrared waves, depths beyond the Hubble deep fields have been achieved with exposures of several weeks, demonstrating the capabilities of the James Webb Telescope.
“The web of the world reminds us of what America can do,” President Biden said.
The first image from the James Webb Telescope. SMACS Galaxy Cluster 0723NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI
The James Webb Telescope is located 1.5 million km from us
The James Webb Telescope is the most advanced and powerful space telescope ever built. The pioneering observatory was created by scientists from NASA, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency.
The telescope weighing over 6.3 tons cost $10 billion to build. It was launched on December 25, 2021. It is located at L2, 1.5 million kilometers from our planet, nearly four times the distance from the Moon. The device has a mirror with a diameter of 6.5 meters and it detects infrared radiation. It is called the successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, which has been in operation for more than 30 years
James Webb Telescopebab/Reuters/Adam Zimenovic
James Webb Telescope Mirrorbab/Reuters/Adam Zimenovic
Main image source: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI

“Devoted organizer. Incurable thinker. Explorer. Tv junkie. Travel buff. Troublemaker.”